Select the Four Main Functions of Cellular Markers.
BioLegend develops and manufactures world- class cutting-edge immunological reagents for biomedical research offered at an outstanding value. Junctions Serve to connect and join two cells together.
Solved Select The Four Main Functions Of Cellular Markers 3 Chegg Com
14 Alveolar bones have a different developmental origin and ossification process compared with long bones and other bones.

. Transport Responsible for facilitated diffusion and active transport. 65 rows Granulosa cells produce estradiol before ovulation and secrete progesterone after ovulation. The unmodified antigen called the H antigen is the characteristic of type O and is.
In scGeneFit the two main. The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells type i and type ii. Select the four main functions of cellular markers TF.
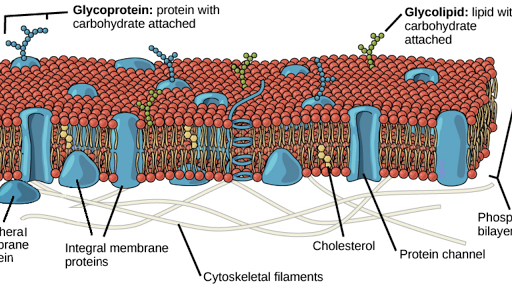
Glycoproteins function in the structure reproduction immune system hormones and protection of cells and organisms. Receiving and transmitting chemical messages to coordinate the. Nature 376 704 1995.
The four main human blood types A B AB O are determined by the oligosaccharide attached to a specific glycolipid on the surface of red blood cells which acts as an antigen. To study human NK cell phenotype and function. We review their content and use your.
Glycoproteins are found on the surface of the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. They supress the activation proliferation and effector function of a wide range of immune cells including autoreactive CD4 or CD8 T Cells which escape negative selection in the thymus NK cells NKT LB and APC. Recognition May function as markers for cellular identification.
The Interactive Cell Markers page shows various cell types and the cell surface markers associated with that cell. Please match the statement to the term that it most accurately describes to test your understanding of the main categories of antigens based on function 1. Membrane proteins can serve a variety of key functions.
Enzymes Fixing to membranes localises metabolic pathways. Due to tooth-derived inflammatory response and occlusal stress stimuli the metabolism and remodeling of alveolar bone are considered to be the most active among the entire skeletal system. The function of type ii is to ________.
MacrophagesDendritic cells engulf process and present antigen on their MHC-I molecules or virally infected cells present viral antigens in their MHC-I molecules CD-8 cells and their T-cell receps recognize that the MHC-I molecule is either missing altered or is wrong and bind to the cell presenting the antigen. Four major immune functions of cell markers 1Attatchment to nonself or foreign antigens 2Binding to cell surface receptors that indicated self such as MHC molecules. The main markers of granulose cells are AMH anti-mullerian hormone Follicle regulatory protein FRP inhibin 118 119 MCAM Melanoma cell adhesion molecule CD146 fibronectin.
Use of such markers is severely restricted by the difficulty accessing the tissue of interest. The major endothelial adhesion molecule controlling cellular junctions and blood vessel formation. Select the four main functions of cellular markers.
The main functions of the digestive system include. The constancy of the chromosome number from one cell generation to the next is maintained through. Besides the classical T-helper 1 and T-helper 2 other subsets have been.
5 Craniofacial bone marrow. VCAM-1 expression in adult hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells is controlled by tissue-inductive signals and reflects their developmental origin. Binding to cell surface receptors that indicate self such as MHC molecules 3.
Naive CD4 T cells are activated after interaction with antigen-MHC complex and differentiate into specific subtypes depending mainly on the cytokine milieu of the microenvironment. Blood 106 8694 2005. Displays useful information such as other names structure distribution function and ligand receptors.
Basophils They are involved in a number of functions such as antigen presentation stimulation and differentiation of. Attachment to nonself or foreign antigens 2. In view of the important contribution of single-cell RNA sequencing for the identification of cell markers we searched PubMed using a list of keywords such as single cell sequencing single cell RNA sequencing single cell RNA-seq and scRNA seq and obtained more than 1000 single-cell sequencing related publications.
CD4 T cells are crucial in achieving a regulated effective immune response to pathogens. The simplistic one-vs-all representation of cell labels to select markers prevents a solution to the. An overview of the function lineage development and key markers of each of these cell types can be found by clicking through to the individual pages listed below.
Bacterial proteins that are potent stimull for T cells Click to select 3. Cell surface markers and molecules that occur in some members of the same species but not in others Click to select 2. Function as cell-surface identity markers Transport specific ions and molecules across the membrane Catalyze specific chemical reactions on the surface of the membrane Receive external chemical messages.
Who are the experts. Their hydrophilic nature allows them to function in the aqueous environment where they act in cell-cell recognition and binding of other molecules. Food moves through the digestive tract due to a process called peristalsis which is the movement of muscles in the GI tract that move the food through the digestive system.
Cellular markers of proliferation differentiation and apoptosis ie programmed cell death can be useful as biomarkers in research focused on nutritional factors and cancer although the measured effect is a general indicator of an altered cell growth regulation effect. Discuss four major immune functions of cell markers. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Memory B cells are formed during the primary response so that upon a secondary antigen exposure a faster and more vigorous antibody response ensues. A molecule that consists of a piece of dna from one organism combined with the dna from a member of another species is called.

Bio 150 Microbiology Chapter 15 Immune Flashcards Quizlet

Comments
Post a Comment